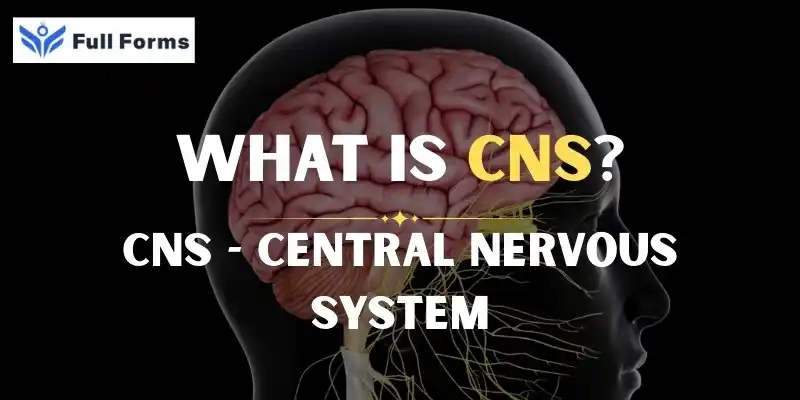
Central Nervous System
(CNS)
Description
The central nervous system is the command center of the body.
In just a single continuous feed in any human’s life, the normal act of breathing, blinking the eyes, and complex decision making accumulate. It is a supreme system that manages all occurrences. This system is many times referred to as the ‘command center’ of the body, as it receives information from both inside the body and outside, processes and reacts to it.
How Our CNS Works
Controls: These include our thoughts, movements, feelings, and even basic functions such as breathing and much more.
Part of a Muscle: Let’s find out more of this interesting and important organ in our bodies.
What Is the Central Nervous System?
The body has two largest divisions in its nervous systems:
- The Central Nervous System
- The Peripheral Nervous System
There are two main components to the central nervous system, or CNS for short:
- The Brain
- The Spinal Cord
Contributing to a complex and efficient network for transmitting messages to and from body parts and processing sensation, they are quite interwoven.
Control Center: The Brain
It is the most intricate part of the body.
It is found inside the head, which is shielded and enclosed by the skull and cerebrospinal fluid.
Generally, the brain contains a few big parts:
- Cerebrum: The largest division of the brain is involved in thinking, memory, reasoning, decision-making, and feelings, as well as some movement control.
- Cerebellum: Located toward the back of the brain, this little piece mainly coordinates balance and fine-tuned muscle activity.
- Brain Stem: It is what joins the brain to the spinal cord and handles really important things like sleep, breathing, and heartbeats.
But it’s teamwork! Each part helps with something that can keep the body running nice and smooth.
The Human Spinal Cord
This organ is in actual fact an elongated slim structure that starts at the base of the mind and descends throughout the backbone.
Comments: The idea of the content stays constant although some changes in terminology have been launched so that anyone can understand the message.
- Carry information to the brain about what the body hears, feels, sees, tastes, and smells
- Receive commands from the brain to move muscles
- Perform some actions as a reflex, without needing the brain’s help (for example, quickly moving your hand away from something hot)
How Does the Central Nervous System Function?
The CNS transfers electric impulses via neurons, which are special nerve cells. That is how it usually works:
- Sensory Input: For example, the eyes, ears, and skin of the body sense things like light, sound, and pressure.
- Processing: This information is transported by the spinal cord to the brain, where it is combined and processed.
- Answer: It returns back relating a message through the spinal cord to the correct parts of the body (muscles, organs) to respond.
All this takes place in a flicker—most of the time, we’re barely aware of it.
The Central Nervous System’s Importance
The CNS is involved in nearly all bodily functions:
- The brain controls muscle movement, voluntary and involuntary.
- It regulates different portions of the senses of sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell.
- Cognition: It generates ideas, recollections, learning, and emotions derive from the brain.
Major health problems are caused when damage or illness that affects the CNS is related to the aforementioned functions.
Common CNS Disorders
Affecting the central nervous system may be as many as all manners of medical conditions, including:
- Stroke: A condition in which blood vessels in the brain become blocked or burst, stopping brain function.
- Parkinson's Disease: A progressive disorder that impairs movement and coordination.
- MS (Multiple Sclerosis): The immune system attacks the nerve’s protective covering—making it difficult for the brain and the rest of the body to communicate.
- Epilepsy: A disorder in which the brain functions so strangely that it causes fits to occur repeatedly.
- Spinal Cord Injuries: Depending on the severity, these may result in partial or complete paralysis.
Such conditions typically warrant maintenance and monitoring for life.
How to Care for Your CNS
Good CNS health is essential for good health in general. Here is how:
- Eat a balanced diet: Get more vitamins, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Exercise regularly: Increase the amount of blood and oxygen that gets to your brain.
- Get plenty of rest: So your brain has time to heal and re-energize.
- Avoid drugs and excess alcohol: These hurt nerve cells in the body.
- Stay mentally active: Read, do puzzles, learn new skills.
- Manage stress: Meditation, hobbies, or therapy can help you learn how to deal with stress.
Final Words
The brain and spinal cord are known as the Central Nervous System.
They control everything a person thinks, feels, and does. Without it, the body would be just as if a machine had no processor.
Knowing how it works and how to take care of it could only mean living a healthier and more conscious way.
Your CNS is always at work behind the scenes, keeping everything in balance.
It controls everything from some of the things we don’t even think about, like breathing and walking, to others we can’t stop thinking about, like dreaming and remembering.
It’s a system you should know about, value, and protect.
